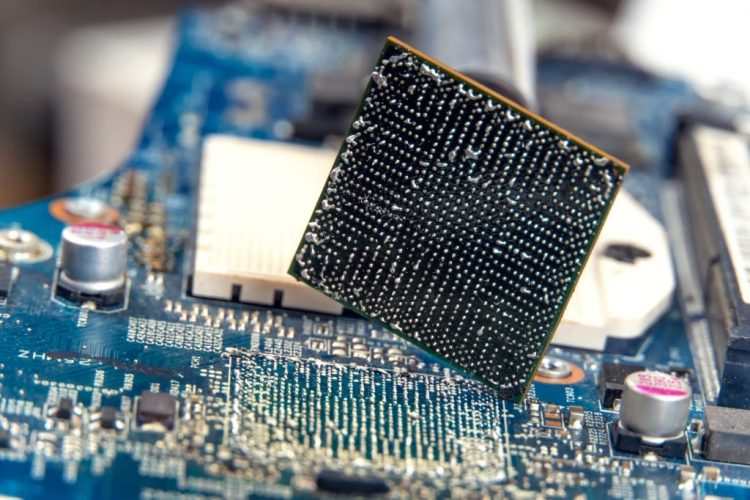
A motherboard is equipped with a lot of slots on which you can install different hardware. Most of these slots are permanently soldered to your motherboard. The BGA (Ball Grid Array) slot is soldered on a motherboard along with the CPU. This type of socket is similar to that of PGA (Pin Grid Array) and LGA (Land Grid Array) meant for connecting the CPU with the motherboard.
BGA Socket
In simple words, the BGA is a type of mounting package used for connecting microprocessors or integrated circuits to a motherboard. Generally, a BGA serves as a bridge between PCB and integrated circuits for conducting electrical signals.
The BGA connectors are soldered permanently by manufacturers alongside the CPU and cannot be replaced. Whereas the LGA and PGA give you more headroom to upgrade your hardware.
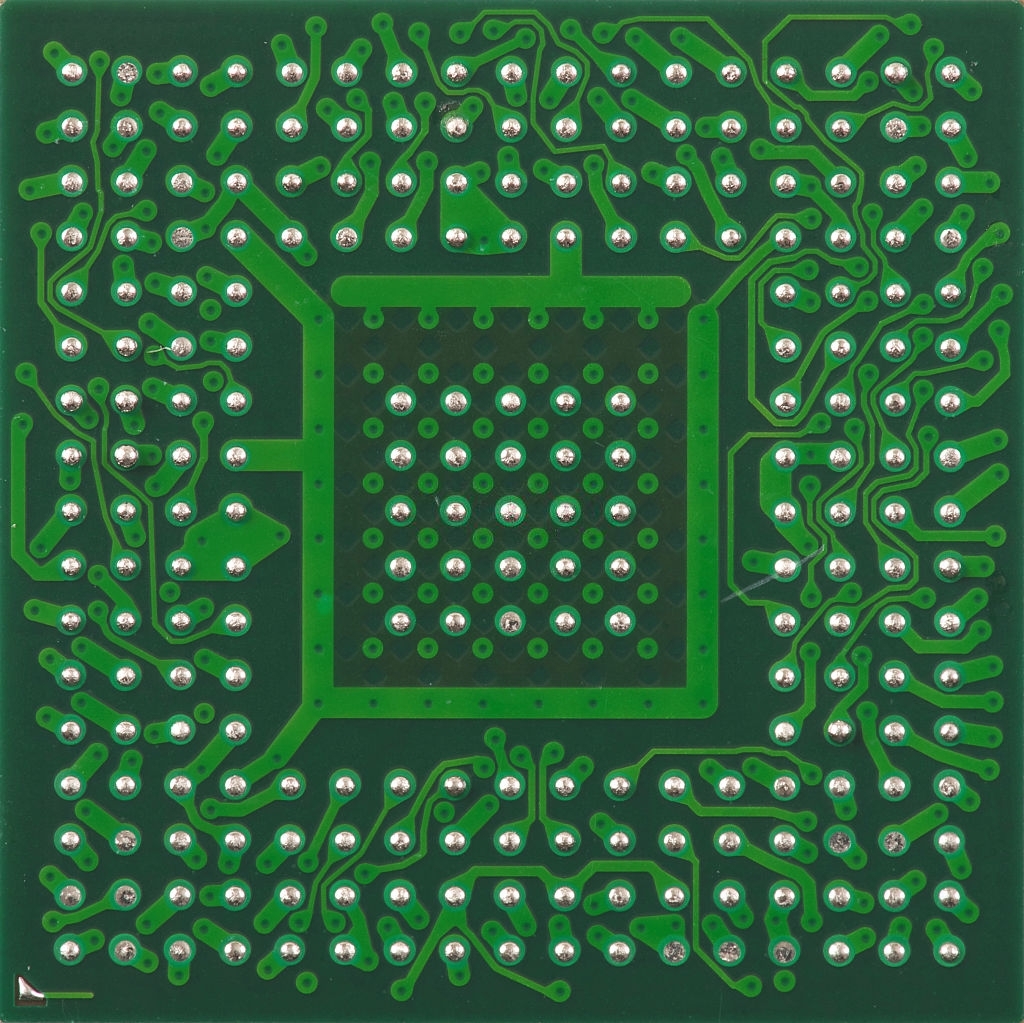
LGA & PGA Socket
In the LGA socket, the pins align with the pads at the bottom of a CPU. No soldering is required in this case, you can easily remove the CPU or upgrade it with a new one whenever you want.
Meanwhile, in PGA, there are vertical slots on a connector that align with the pins on a CPU. Same as an LGA socket, a PGA connector doesn’t need any soldering work at all.
Actually, a BGA socket has descended down from a PGA socket which comprises one face covered in pins or grids. However, in BGA, the pins are now replaced by pads each having a tiny solder ball stuck to its at the bottom of the package.
Advantages of BGA
Here are the main benefits of using BGA on PCBs.
- High-Density
- Low-Inductance
- Heat Conduction
Disadvantages of BGA
Some cons of BGA are as follows:
- Lack of compliance
- Difficulty to inspect
- Difficulty in circuit development
- Expensive equipment needed to solder BGA on a motherboard
Conclusion
We hope you know that what type of socket is soldered along with the CPU on a motherboard. Obviously, it is the BGA socket that plays a vital role in generating electrical signals on a motherboard.